External Secrets
External Secrets is an Installable that supports syncing secrets from external secret management systems like AWS Secrets Manager and Azure Key Vault into Kubernetes Secret resources.
For a broader guide on using secrets with PlatformApplications, check out the guide here.
This page provides a quick guide for adding secrets to Platform Applications and pulling content from cloud secret stores. For more context around secrets, refer to the complete guide above.
Specify Secret Name
Edit your PlatformApplication manifest to include a spec.secrets section with the name of the secret you want to sync from your cloud secret store.
# .platform/kubernetes/base/application.yaml
apiVersion: meta.p6m.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PlatformApplication
metadata:
name: sample-service
spec:
secrets:
- name: sample-service
config: #...
deployment: #...
Add External Secret Content
- Azure KeyVault
- AWS Secret Store
Check out the Azure Docs for more information
- Once your application is deployed, the
PlatformApplicationoperator will automatically create an Azure Key Vault based on the application name, note this name might be abbreviated.- To get the exact name, check the
AzureKeyVaultresource in ArgoCD, the field status.values.resourceId will have the exact name.
- To get the exact name, check the
- Add your Secret to the KeyVault, in the Azure portal by clicking on the specified KeyVault and then going to Objects -> Secrets and clicking Generate/Import
- Set your Secret Name to match what you decided on above (spec.secrets[].name, ex: "sample-service") and set the Secret Value using a JSON format:
Remember each key will be loaded as a separate environment variable
{
"KEY_NAME_1": "VALUE_1",
"KEY_NAME_2": "value_2",
"FOO": "BAR"
}
Required Azure Role Assignment
To write secrets to your Key Vault, you need the Azure Key Vault Officer role assigned to your user account:
# This command must be run by an Azure administrator
az role assignment create \
--role "Key Vault Officer" \
--assignee "your-email@company.com" \
--scope "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}/resourceGroups/{resource-group}/providers/Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/{keyvault-name}"
Note: Only Azure administrators can assign this role. Contact your platform team if you need access to write secrets to your Key Vault.
Alternative: Request Secret Creation
If you don't have Key Vault Officer access, you can:
- Submit a request to your platform team to create the secrets
- Provide the secret values in a secure manner
- Specify the secret names that match your PlatformApplication configuration
Check out the AWS Docs for more information
-
Once your application is deployed with a secret listed, the
PlatformApplicationoperator will automatically create aSecretStorewhich is responsible for forming the connection to AWS Secrets Manager.- You can check the region and other details in ArgoCD by looking at the
SecretStoreresource created for your application.
- You can check the region and other details in ArgoCD by looking at the
-
Go to AWS Secrets Manager in the AWS Console, and make sure to be in the region indicated by the
SecretStore. By default this is the region your cluster is deployed in. -
Click Store New Secret
-
Select Other type of secret and add key-value pairs to your secret. You could also use plain text and provide JSON:
{
"KEY_NAME_1": "VALUE_1",
"KEY_NAME_2": "value_2",
"FOO": "BAR"
}Remember each key will be loaded as a separate environment variable
-
Click Next, set your Secret name to match what you decided on above (spec.secrets[].name, ex: sample-service) and Save.
Verify in ArgoCD
Now that your cloud secret is set up, we can go back to ArgoCD and make sure that it is being pulled into Kubernetes.
- Verify your
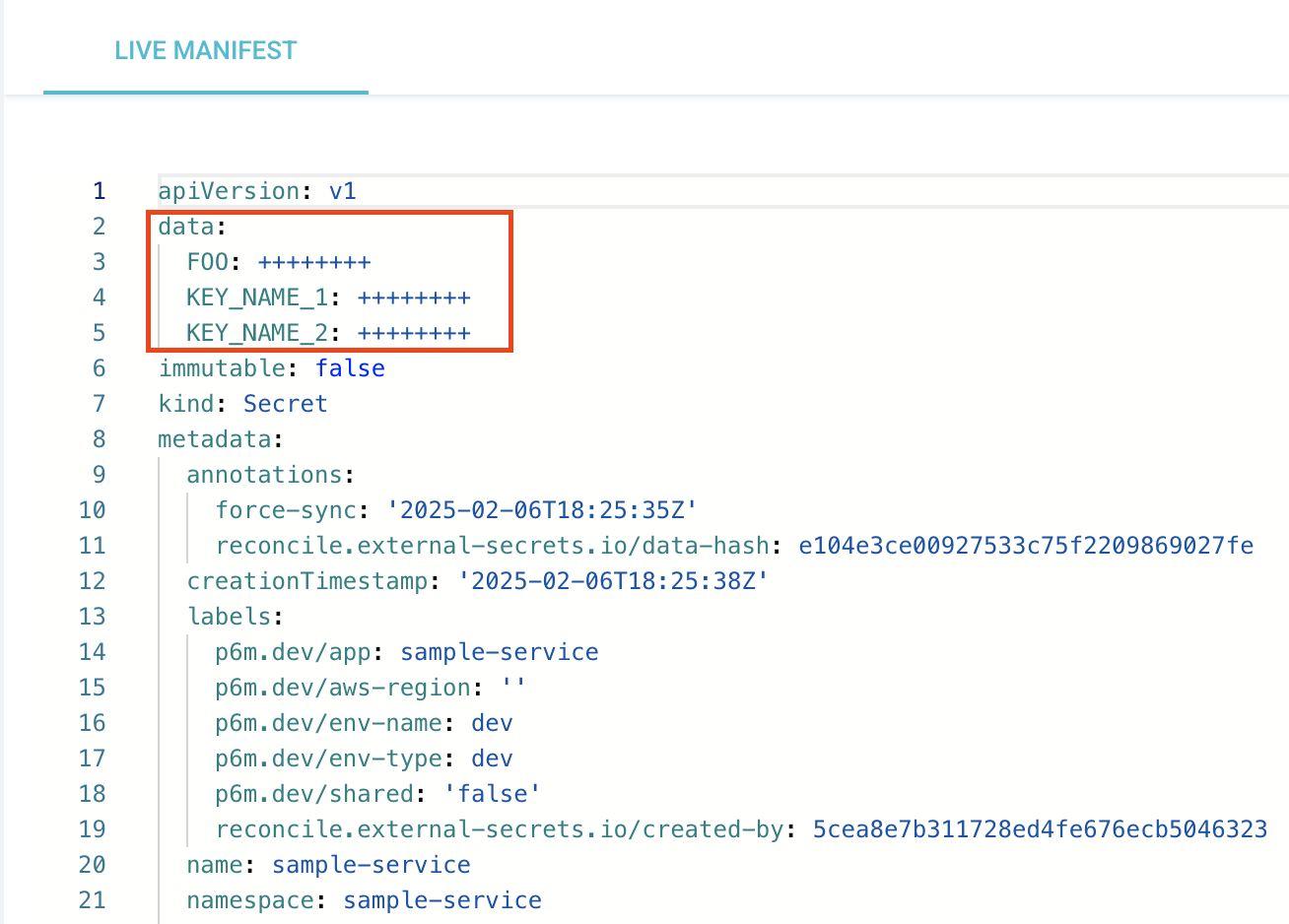
ExternalSecretis healthy and theSecretit creates has your data in ArgoCD.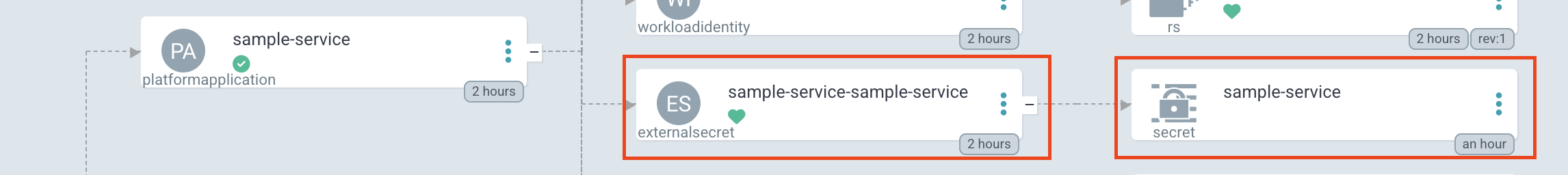 Secrets are secret
Secrets are secretArgoCD will mask the values in the UI, but be cautious when sharing screenshots or logs.
- Restart your
Deployment, so these key-value pairs are injected into your pods as Environment Variables