Secret Injection
This example builds on Configuration Management by adding secret injection from a cloud secret store.
What You'll Learn
In this lesson, you'll learn:
- How to inject secrets from cloud secret stores
- Secret format and naming conventions
- Secret rotation
- Security best practices
What Gets Created
In addition to resources from Configuration Management, the platform creates:
SecretStore- connection to cloud providerExternalSecret- syncs a specific secret from the cloud- Kubernetes
Secret- created by theExternalSecretand automatically mounted by the Platform Application Operator - IAM roles/permissions - automatically configured
What Changed
Added the spec.secrets section:
apiVersion: meta.p6m.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PlatformApplication
metadata:
name: demo-http-echo
namespace: demo-http-echo
labels:
p6m.dev/app: demo-http-echo
spec:
config:
LOG_LEVEL: debug
HTTP_PORT: "8080"
ENVIRONMENT: dev
APP_NAME: demo-http-echo
# NEW
secrets:
- name: super-secret-data # Must exist in cloud secret store
# NEW
deployment:
image: mendhak/http-https-echo:31
ports:
- port: 8080
protocol: http
readinessProbe:
port: 8080
path: /
networking:
ingress:
enabled: true
path: /
gateway: public-open
Create Secret in the Cloud
We have a focused guide for creating secrets in your preferred cloud provider, check it out here.
Deploy Steps
- ArgoCD
- kubectl
ArgoCD automatically updates to your PlatformApplication after the Platform Dispatch Action to update your .platform repository is run.
Let's use the Kinds filter to locate our ExternalSecrets, Secrets, and SecretStore which are the new objects that will be created.
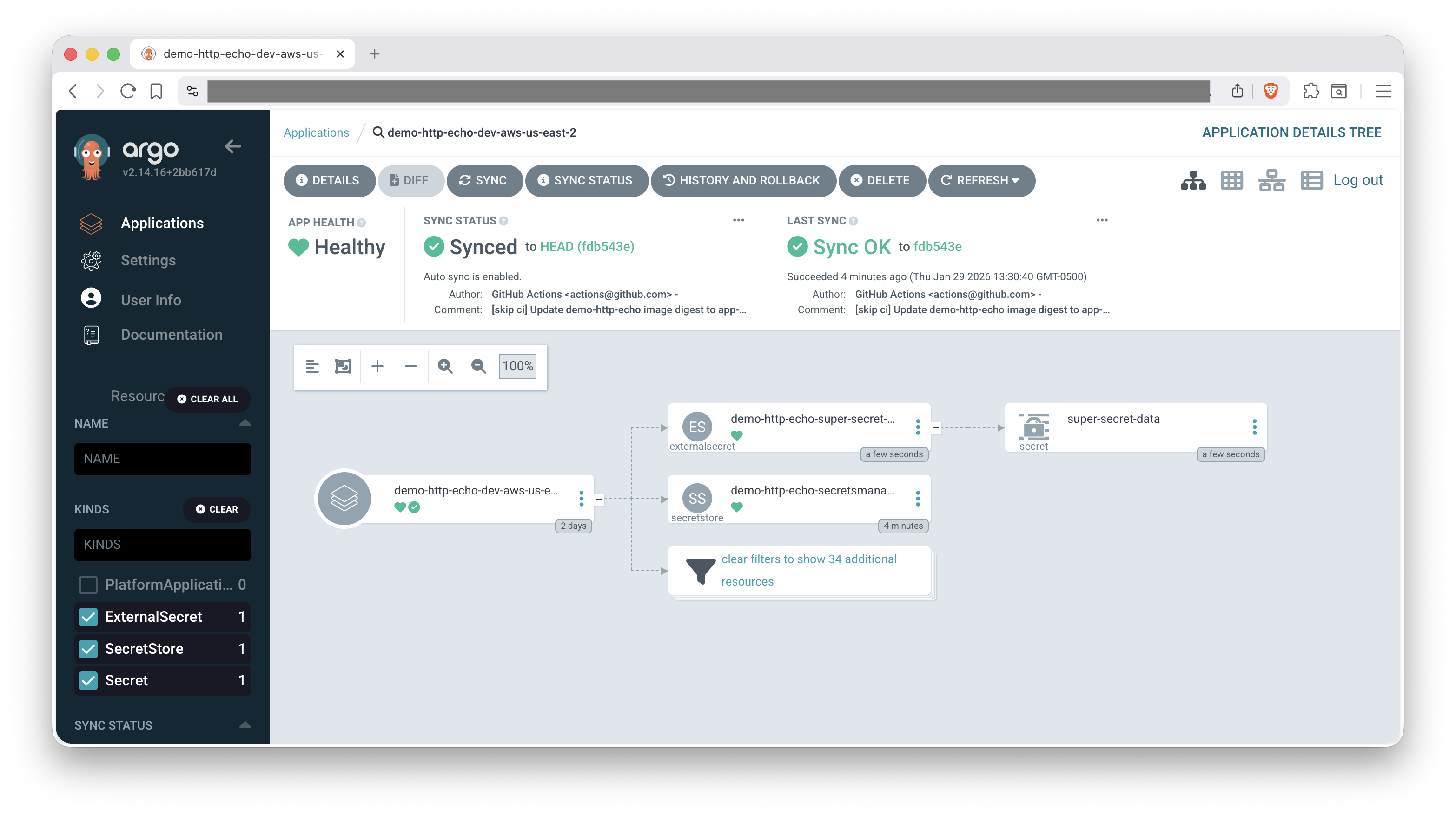
- Check out our ArgoCD Cheat Sheet for tips on interacting with ArgoCD.
- For more information on setting up ArgoCD for Platform Applications, see the ArgoCD Deployment Tutorial.
# Apply the Platform Application
kubectl apply -f application.yaml
Verify the ExternalSecret was created with our name super-secret-data
kubectl get externalsecret -n demo-http-echo
# NAME STORE REFRESH INTERVAL STATUS READY
# demo-http-echo-super-secret-data demo-http-echo-secretsmanager 1m SecretSynced True
# dockerconfig secretsmanager 1m0s SecretSynced True
Check that secret synced successfully (events at the bottom)
kubectl describe externalsecret demo-http-echo-super-secret-data -n demo-http-echo
# Name: demo-http-echo-super-secret-data
# ...
# Kind: ExternalSecret
# Metadata:
# ...
# Events:
# Type Reason Age From Message
# ---- ------ ---- ---- -------
# Normal Created 10m external-secrets Created Secret
How Secrets Work
The platform uses the External Secrets Operator to:
- Fetch secrets from your cloud secret store
- Create Kubernetes Secrets with the secret data
- Inject as environment variables into your pods
Secret Format Requirements
Secrets must be stored as key-value pairs (JSON object):
{
"API_KEY": "abc123",
"DATABASE_PASSWORD": "xyz789",
"OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET": "secret456"
}
Keys become environment variable names (use UPPERCASE_WITH_UNDERSCORES).
Want to dive deeper? See Secret Injection - Details for cloud setup procedures, verification steps, and security best practices.
You've Completed the Tutorial! 🎉
Further Learning:
- Cloud Resources with Crossplane
- Autoscaling with KEDA
- Service Mesh configuration
- Observability integration
Check the Platform Documentation for advanced topics.
Troubleshooting
For common issues and solutions, see the Troubleshooting Guide.
Specific sections that may be helpful:
Cleanup
Check out the Cleanup Instructions from the Basic Deployment lesson to remove all resources created in this walkthrough.
Make sure to also delete any secrets created in your cloud secret store to avoid incurring costs.
Related Documentation
- External Secrets Operator - ESO documentation
- AWS Secrets Manager - AWS secret management
- Azure Key Vault - Azure secret management
- Kubernetes Secrets - Understanding Secrets