Ingress Configuration
This example builds on Basic Deployment by adding ingress configuration to expose your application to traffic outside of the cluster.
What You'll Learn
In this lesson, you'll learn:
- How to expose your application to the internet
- Ingress configuration options
- Hostname patterns and DNS
- Visibility (public vs private)
- Authentication (OIDC)
What Gets Created
In addition to the resources from Basic Deployment, the platform creates:
- HTTPRoute (Gateway API) or VirtualService (Istio)
- Gateway configuration
- DNS entries (automatic)
- TLS certificates (automatic)
What Changed
Added the spec.networking.ingress section:
apiVersion: meta.p6m.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PlatformApplication
metadata:
name: demo-http-echo
namespace: demo-http-echo
labels:
p6m.dev/app: demo-http-echo
spec:
deployment:
image: mendhak/http-https-echo:31
ports:
- port: 8080
protocol: http
readinessProbe:
port: 8080
path: /
# NEW
networking:
ingress:
enabled: true
path: /
gateway: public-open
# NEW
Gateway Selection
If you do not specify a gateway (spec.networking.ingress.gateway), the platform will use the one assigned by the Administrator as the Environment default.
Check out the Gateway Selection Details for more information on choosing the right gateway for your use case.
Deploy Steps
- ArgoCD
- kubectl
ArgoCD automatically updates to your PlatformApplication after the Platform Dispatch Action to update your .platform repository is run.
For more information on setting up ArgoCD for Platform Applications, see the ArgoCD Deployment Tutorial.
Find Your Application's URL
To find your application's URL, use ArgoCD to find the HTTPRoute (spec.hostnames[]) or VirtualService (spec.hosts[]) created for your application, then check the spec appropriate field.
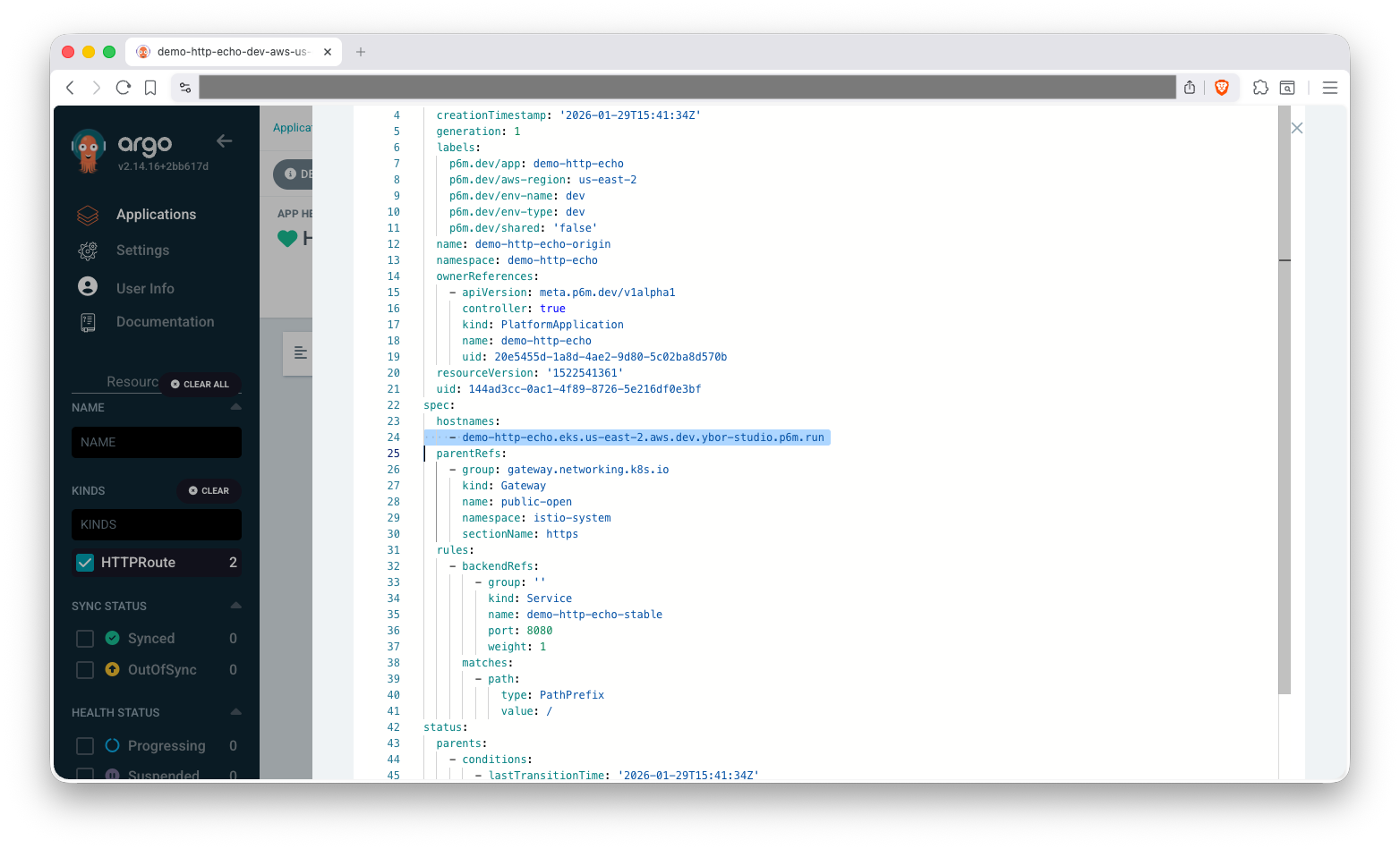
Optionally you can use kubectl to check the diff with existing resources
kubectl diff -f application.yaml
## kubectl automatically finds the resource(s) based on the name and namespace
To apply the updated PlatformApplication just apply the manifest again:
kubectl apply -f application.yaml
You can get (with the watch option) for the HTTPRoutes or VirtualServices to be created so you know when it's ready:
kubectl get httproute -n demo-http-echo --watch
# NAME HOSTNAMES AGE
# demo-http-echo-custom-domains ["demo-http-echo.cdn.aws.dev.ybor-studio.p6m.run"] 1m
# demo-http-echo-origin ["demo-http-echo.eks.us-east-2.aws.dev.ybor-studio.p6m.run"] 1m
# Or for Istio:
# kubectl get virtualservice -n demo-http-echo --watch
Find Your Application's URL
Once the resources are created, you can find your application's URL:
kubectl get httproute demo-http-echo-origin -n demo-http-echo -o jsonpath='{.spec.hostnames}'
# ["demo-http-echo.eks.us-east-2.aws.dev.ybor-studio.p6m.run"]
# Or for Istio:
# kubectl get virtualservice demo-http-echo-origin -n demo-http-echo -o jsonpath='{.spec.hosts}'
Test Access
Once DNS has propagated, test access from outside the cluster using curl.
curl https://demo-http-echo.eks.us-east-2.aws.dev.ybor-studio.p6m.run
# {
# "path": "/",
# "headers": {
# "host": "demo-http-echo.eks.us-east-2.aws.dev.ybor-studio.p6m.run",
# ...
# "os": {
# "hostname": "demo-http-echo-b994d5d67-gpdxz"
# },
# "connection": {}
# }
You can see the pod name in the response, showing that the request did go where we wanted.
Custom Hostnames
PlatformApplications can be configured with custom hostnames by adding hosts to spec.networking.ingress.hostnames[]. Since this requires Certificates to be configured as well, check out our specific guide here (Coming Soon).
Configuration Options
- Visibility (PublicIP / PrivateIP)
- OIDC authentication
- Custom hostnames
- Path-based routing
- Gateway selection
Want to dive deeper? See Ingress Configuration - Details for comprehensive verification procedures, gateway selection guidance, and advanced configuration options.
Next Steps
- Configuration Management - Add environment variables
- Secret Injection - Inject secrets from cloud secret stores
Troubleshooting
For common issues and solutions, see the Troubleshooting Guide.
Specific sections that may be helpful:
Cleanup
Check out the Cleanup Instructions from the Basic Deployment lesson to remove all resources created in this walkthrough.
Related Documentation
- Gateway API Documentation - Understanding Gateway API
- Istio Virtual Services - Istio routing